
LIC IPO caught the attention of the Indian masses and created a buzz across the stock market like never before. Since LIC IPO was announced in the 2021-22 financial budget, talks about disinvestment strategies are around the corner. Apart from liberlaising the insurance sector, LIC IPO is a huge step in the disinvestment for Indian Government.
What exactly is disinvestment and what it has got to do with IPO?
Here we are to give you an overview of what disinvestment is. Read along to know.
In general, disinvestment is a strategy by which an organistaion ( or government) offloads or disposes of an asset or a partial stake in the asset. Disinvestment by the government means the market activity through which the government conducts sale or liquidation (full or partial) of government-owned assets. Such assets usually refer to the government’s ownership stake in Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) and State Public Sector Enterprises (SPSEs), but are not limited to that. Government assets also include project undertakings and other fixed assets.
Disinvestment was first introduced in India in the budget speech of FY1991-92..Starting with the projected disinvestment of Rs 2500 crore in 1991-92, Indian government has set a disinvestment target of Rs65,000 crore for the financial year 2022-23. But, why does government disinvests its assets? Read further to know

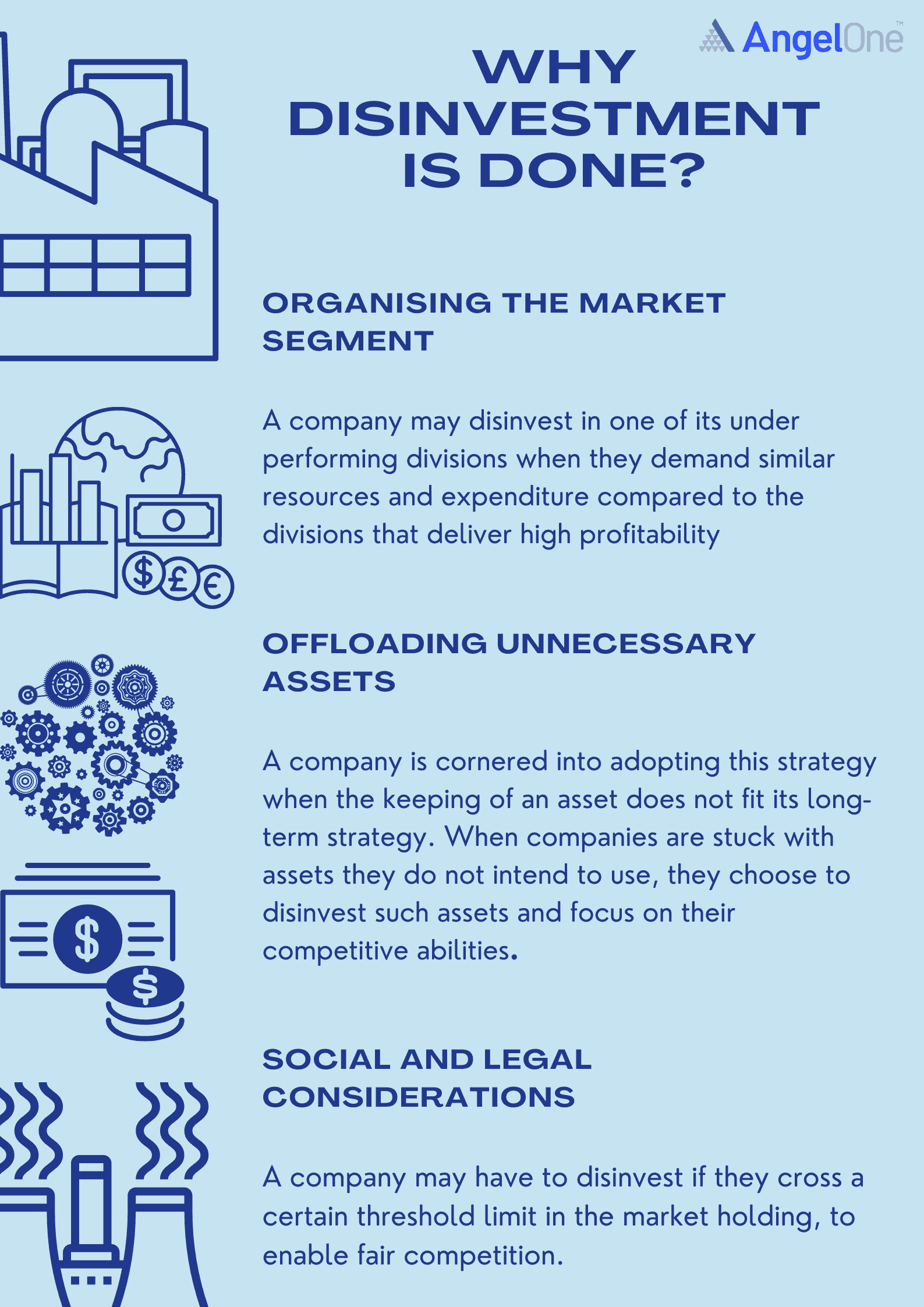
As per the ‘Disinvestment Policy’ of the Government of India (GOI), following are the main objectives of disinvestment in India:
| Parameter | Disinvestment | Privatization |
| Means | Government sells only a minor stake to a private entity and holds the majority stake with itself | Government sells an entire subsidiary or a majority stake, which results in the government losing its control and ownership |
| Control | Dilution of control, the government retains control | Transfer of control, control changes hands |
| Shareholding | Government retains more than 50% | Government retains less than 50% or nil |
| Scope | Narrow | Wide |
| Examples | Rail Vikas Nigam Ltd., IRCTC, Coal India Limited, HAL, BHEL, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd., LIC, etc. | Maruti Udyog, Bharat Aluminium Company (BALCO), Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL), Air India, etc. |
Disinvestment of an asset can be done through any of the following means:
Some of the benefits of disinvestment, irrespective of the approach are as follows:
In 1999, the Department of Disinvestment was set up as a separate department and later renamed as Department of Investment and Public Asset Management, functioning under the Ministry of Finance at present. Disinvestment targets are set under each Union Budget, and every year the targets change. The government takes the final decision on whether to raise the divestment target or not.
Disinvestment has tended to achieve mixed results for the Government of India in terms of receipts and estimated projections. For the FY 2022-23, the targets of disinvestment are downward revised. After a 3.5% stake sale in LIC through IPO, the big tickets that are in pipeline for FY 2022-23 are Shipping Corporation of India (SCI) and IDBI Bank. We hope we can look forward to more investment opportunities if there are further disinvestments in future.
Disclaimer:This blog is exclusively for educational purposes and source for statistical data and note approval is valid for 180 calendar days from date of approval.
Published on: May 19, 2022, 2:11 PM IST
We're Live on WhatsApp! Join our channel for market insights & updates